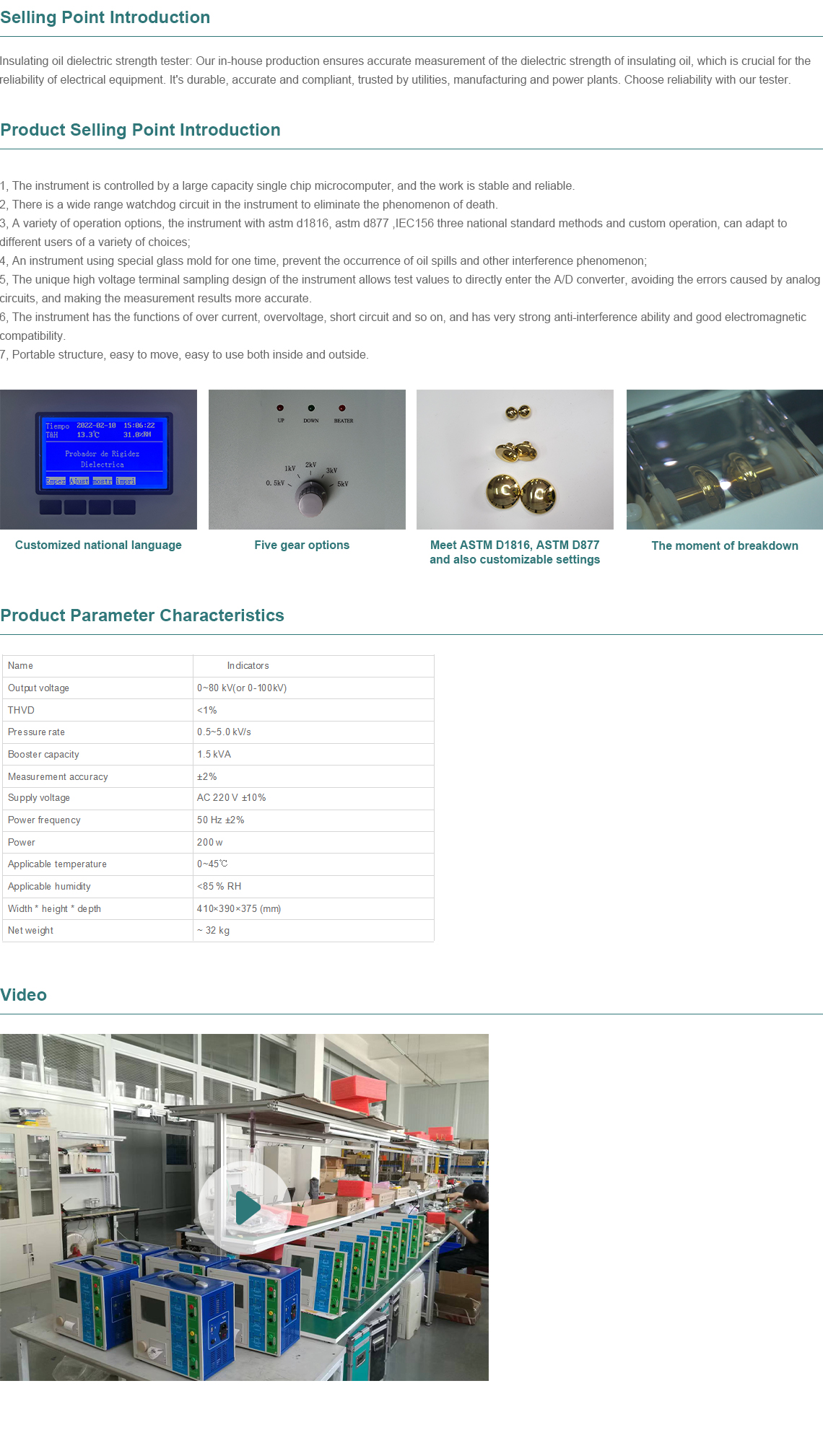
 English
English



-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
dielectric loss angle test
Understanding Dielectric Loss Angle Test A Comprehensive Overview
The dielectric loss angle test is a critical examination used primarily in electrical engineering and material science to assess the insulating properties of dielectric materials. This test measures the energy loss in a dielectric material when subjected to an alternating electric field. Understanding dielectric loss is essential for ensuring the reliability and efficiency of electrical systems, and the dielectric loss angle provides important insight into the performance of insulation materials.
What is Dielectric Loss?
Dielectric loss refers to the energy that is dissipated as heat when an electric field is applied to a dielectric material. This phenomenon occurs due to the lagging of electric displacement behind the electric field in a dielectric medium. Specifically, the dielectric loss is closely associated with the material's polar molecular structure, which responds to the electric field and causes frictional losses at the molecular level. The result is a loss angle that quantifies the phase difference between the applied voltage and the resultant current.
Dielectric Loss Angle
The dielectric loss angle, often represented by the symbol δ (delta), is a critical parameter derived from the complex impedance of the dielectric. Mathematically, it is defined as the angle whose tangent gives the ratio of the dielectric loss to the dielectric storage or energy component. Formally, it can be expressed as
\[ \tan(δ) = \frac{W_d}{W_e} \]
Where - \( W_d \) is the dielectric loss energy. - \( W_e \) is the dielectric stored energy.
The dielectric loss angle is a vital indicator of a material's dielectric quality. A small loss angle indicates good insulation properties, whereas a larger angle suggests higher losses, implying poorer performance in insulating applications.
Importance of the Dielectric Loss Angle Test
dielectric loss angle test
1. Material Evaluation The dielectric loss angle test is instrumental in evaluating the performance of various dielectric materials, including polymers, ceramics, and composite materials. By analyzing the dielectric loss angle, engineers can determine the suitability of materials for specific applications, such as capacitors, insulators, and transformers.
2. Predicting Lifespan High dielectric loss, indicated by a larger loss angle, often correlates with a shorter lifespan for electrical components. This knowledge helps manufacturers produce more reliable products by selecting suitable materials or improving processing methods to enhance dielectric performance.
3. Quality Control The test is also essential in quality assurance processes for electrical manufacturing. By conducting dielectric loss angle tests on production lots, manufacturers can detect material defects, inconsistencies, or degradation that might compromise the dielectric properties of their products.
4. Thermal Management Understanding dielectric loss angles provides insight into the thermal behavior of materials under operational conditions. This information is crucial for thermal management in electronic systems, as it aids in designing cooling systems that mitigate overheating.
Testing Procedure
The dielectric loss angle test typically involves using sophisticated equipment like a dielectric spectrometer or an LCR meter. The procedure includes applying an alternating electric field to the dielectric sample and measuring the resulting current. The test frequently entails multiple frequency ranges to understand the dielectric behavior under different operational conditions.
Applications
The dielectric loss angle test finds applications in various fields - Power Systems Used to assess the insulation quality of high-voltage cables, transformers, and switchgear. - Electronics Helps in selecting materials for capacitors and circuit boards where insulation stability is vital. - Telecommunications Ensures the reliability of materials used in signal transmission and reception.
Conclusion
The dielectric loss angle test is a fundamental procedure in evaluating the performance of dielectric materials. By understanding the dielectric loss angle and its implications, engineers and material scientists can enhance the reliability, efficiency, and lifespan of electrical systems. As technology advances, the importance of this test will continue to grow, supporting the development of new materials and systems in an increasingly electrified world. The correlation between dielectric loss angle and material performance emphasizes the need for robust testing methods to foster innovation and safety in electrical engineering.
-
Testing Equipment Industry Sees Major Advancements in 2025: Smart & Precision Technologies Lead the WayNewsJun.06,2025
-
Applications of Direct Current Generators in Renewable Energy SystemsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Hipot Tester Calibration and Accuracy GuidelinesNewsJun.05,2025
-
Digital Circuit Breaker Analyzer Features and BenefitsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Benefits of Real-Time Power Quality Monitoring Devices for Industrial EfficiencyNewsJun.05,2025
-
Earth Fault Loop Testing in High-Rise Building Electrical SystemsNewsJun.05,2025



