 English
English



-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
Testing Partial Discharge in Current Transformers for Enhanced Performance and Reliability
Partial Discharge Test of Current Transformers An Overview
Current transformers (CTs) are essential components in electrical power systems, serving to transform high currents into lower, manageable levels while maintaining accuracy for measurement and protection purposes. However, like all electrical equipment, CTs are vulnerable to insulation failures, which can lead to severe operational disruptions and safety hazards. One critical method for assessing the health of a current transformer is the Partial Discharge (PD) test. This article explores the significance, methodology, and interpretation of PD tests in the context of current transformers.
Understanding Partial Discharge
Partial discharge refers to the localized dielectric breakdown of insulation materials. It occurs within an insulation system when the electric field strength exceeds the material's dielectric strength, but it does not result in a complete insulation failure. PD can occur in solid, liquid, or gaseous insulation and is often symptomatic of insulation deterioration, which may eventually lead to catastrophic failure if unchecked.
In current transformers, partial discharges can arise from imperfections in the insulation, such as voids, cracks, or impurities. The occurrence of PD signals potential weaknesses in the insulation that need to be monitored and addressed to ensure the long-term reliability of the transformer.
Importance of PD Testing
Performing PD tests on current transformers is critical for several reasons
1. Condition Assessment Regular PD testing allows engineers to assess the condition of the insulation within CTs. By identifying and quantifying PD activity, operators can gauge the likelihood of insulation failure.
2. Preventative Maintenance Early detection of insulation problems through PD measurements enables operators to take corrective actions before a significant failure occurs. This proactive approach can save costs and reduce the risk of unexpected outages.
3. Regulatory Compliance Many industries and jurisdictions require regular testing of electrical equipment to ensure compliance with safety and reliability standards. Partial discharge testing can help meet these regulatory requirements.
4. Performance Optimization Understanding the insulation condition through PD testing can help optimize the operation and performance of current transformers, thereby improving overall system reliability.
Methodology of PD Testing
partial discharge test of current transformer
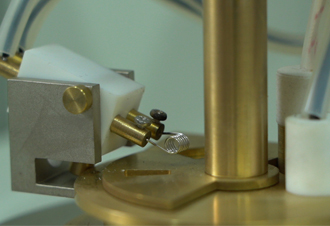
The PD testing of current transformers involves several key steps
1. Test Equipment Setup Specialized equipment is used to detect and measure PD activity. This includes PD detectors, high-frequency current transformers, and oscilloscopes.
2. Test Protocol The current transformer is subjected to a voltage stress, often at a level above its normal operating voltage, to induce partial discharge phenomena. The testing is typically performed under controlled conditions to ensure accurate readings.
3. Data Collection The PD activity is monitored and recorded throughout the test. Data is collected in the form of pulse sizes, frequencies, and patterns, which are indicative of the insulation condition.
4. Analysis The collected data is analyzed using established criteria to determine the severity of the detected partial discharges. Factors such as the magnitude and repetitive nature of PD pulses can indicate the likelihood of insulation failure.
Interpreting PD Test Results
Interpreting PD test results requires a thorough understanding of the electrical environment and the properties of the current transformer under test. A low level of PD activity is generally acceptable, but increasing levels or a marked change from baseline measurements can be cause for concern.
The results are often classified into three categories
- Acceptable Little or no PD activity is detected, indicating good insulation integrity. - Caution Some PD activity is observed, suggesting potential issues that need monitoring over time. - Action Required High levels of PD activity are detected, necessitating immediate investigation and possible intervention.
Conclusion
The partial discharge test is a vital tool in the maintenance and operation of current transformers. By identifying insulation weaknesses early on, operators can ensure the reliability and longevity of their electrical systems. As technology advances, the methods and tools for PD testing continue to improve, enhancing our ability to understand and mitigate risks associated with insulation failures. In a world that increasingly relies on stable and efficient electrical power, the role of PD testing in current transformers cannot be overstated. Regular PD assessments are an investment in the safety and reliability of electrical infrastructure, ultimately safeguarding both equipment and operational continuity.
-
Testing Equipment Industry Sees Major Advancements in 2025: Smart & Precision Technologies Lead the WayNewsJun.06,2025
-
Applications of Direct Current Generators in Renewable Energy SystemsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Hipot Tester Calibration and Accuracy GuidelinesNewsJun.05,2025
-
Digital Circuit Breaker Analyzer Features and BenefitsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Benefits of Real-Time Power Quality Monitoring Devices for Industrial EfficiencyNewsJun.05,2025
-
Earth Fault Loop Testing in High-Rise Building Electrical SystemsNewsJun.05,2025



