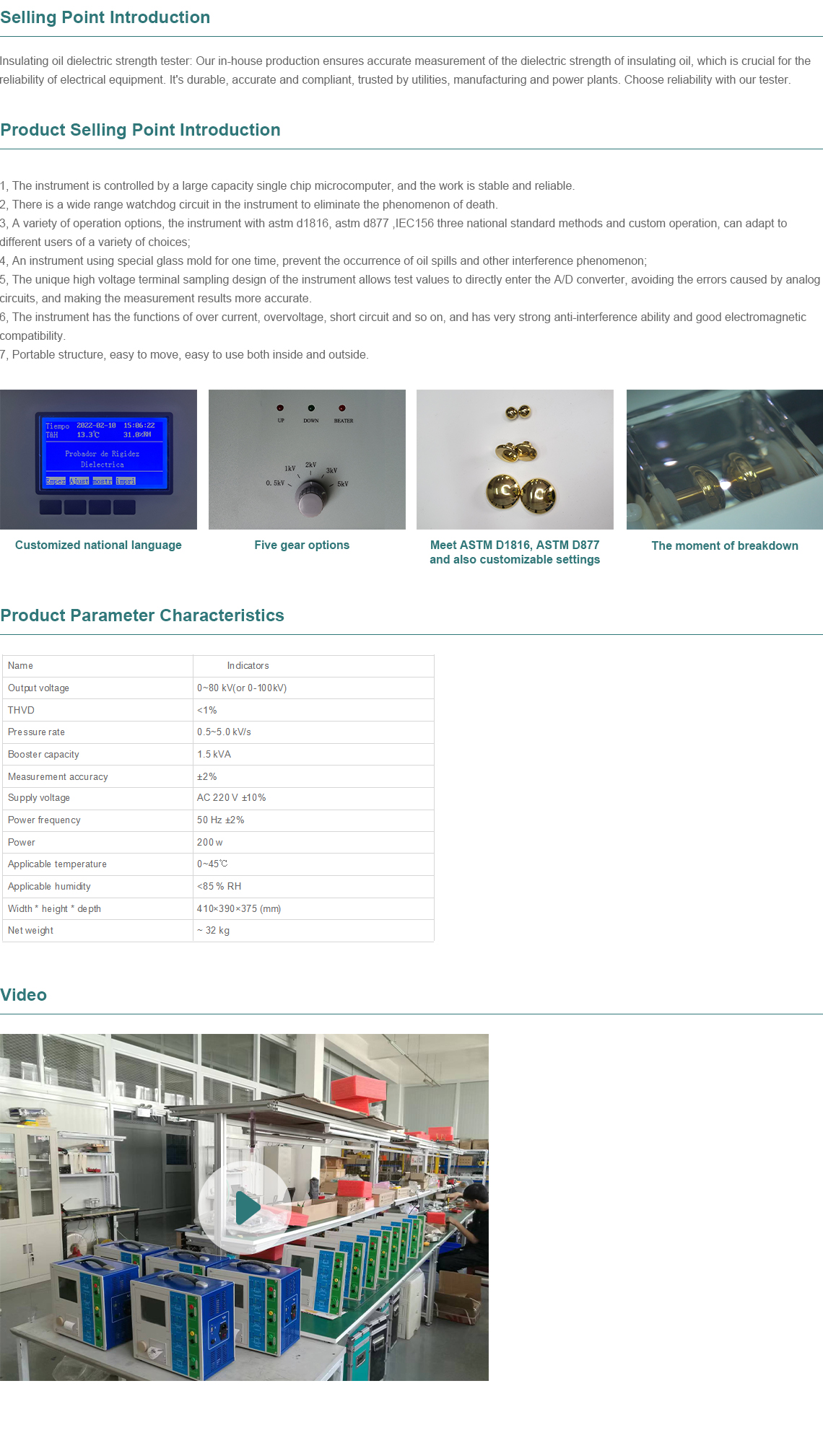
TEL:
+86-0312-3189593
 English
English

Telephone:0312-3189593

Email:sales@oil-tester.com

-
 Afrikaans
Afrikaans -
 Albanian
Albanian -
 Amharic
Amharic -
 Arabic
Arabic -
 Armenian
Armenian -
 Azerbaijani
Azerbaijani -
 Basque
Basque -
 Belarusian
Belarusian -
 Bengali
Bengali -
 Bosnian
Bosnian -
 Bulgarian
Bulgarian -
 Catalan
Catalan -
 Cebuano
Cebuano -
 China
China -
 China (Taiwan)
China (Taiwan) -
 Corsican
Corsican -
 Croatian
Croatian -
 Czech
Czech -
 Danish
Danish -
 Dutch
Dutch -
 English
English -
 Esperanto
Esperanto -
 Estonian
Estonian -
 Finnish
Finnish -
 French
French -
 Frisian
Frisian -
 Galician
Galician -
 Georgian
Georgian -
 German
German -
 Greek
Greek -
 Gujarati
Gujarati -
 Haitian Creole
Haitian Creole -
 hausa
hausa -
 hawaiian
hawaiian -
 Hebrew
Hebrew -
 Hindi
Hindi -
 Miao
Miao -
 Hungarian
Hungarian -
 Icelandic
Icelandic -
 igbo
igbo -
 Indonesian
Indonesian -
 irish
irish -
 Italian
Italian -
 Japanese
Japanese -
 Javanese
Javanese -
 Kannada
Kannada -
 kazakh
kazakh -
 Khmer
Khmer -
 Rwandese
Rwandese -
 Korean
Korean -
 Kurdish
Kurdish -
 Kyrgyz
Kyrgyz -
 Lao
Lao -
 Latin
Latin -
 Latvian
Latvian -
 Lithuanian
Lithuanian -
 Luxembourgish
Luxembourgish -
 Macedonian
Macedonian -
 Malgashi
Malgashi -
 Malay
Malay -
 Malayalam
Malayalam -
 Maltese
Maltese -
 Maori
Maori -
 Marathi
Marathi -
 Mongolian
Mongolian -
 Myanmar
Myanmar -
 Nepali
Nepali -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Norwegian
Norwegian -
 Occitan
Occitan -
 Pashto
Pashto -
 Persian
Persian -
 Polish
Polish -
 Portuguese
Portuguese -
 Punjabi
Punjabi -
 Romanian
Romanian -
 Russian
Russian -
 Samoan
Samoan -
 Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic -
 Serbian
Serbian -
 Sesotho
Sesotho -
 Shona
Shona -
 Sindhi
Sindhi -
 Sinhala
Sinhala -
 Slovak
Slovak -
 Slovenian
Slovenian -
 Somali
Somali -
 Spanish
Spanish -
 Sundanese
Sundanese -
 Swahili
Swahili -
 Swedish
Swedish -
 Tagalog
Tagalog -
 Tajik
Tajik -
 Tamil
Tamil -
 Tatar
Tatar -
 Telugu
Telugu -
 Thai
Thai -
 Turkish
Turkish -
 Turkmen
Turkmen -
 Ukrainian
Ukrainian -
 Urdu
Urdu -
 Uighur
Uighur -
 Uzbek
Uzbek -
 Vietnamese
Vietnamese -
 Welsh
Welsh -
 Bantu
Bantu -
 Yiddish
Yiddish -
 Yoruba
Yoruba -
 Zulu
Zulu
2 月 . 15, 2025 23:20
Back to list
transformer dc winding resistance tester
The winding resistance test of current transformers (CTs) plays a crucial role in ensuring the reliability and accuracy of power systems. As a seasoned professional in the field of electrical testing and diagnostics, I aim to provide a comprehensive guide on this vital process.
The test procedure includes connecting the micro-ohmmeter across the CT’s winding terminals and then recording the resistance reading. Comparing these measurements with the manufacturer's specifications helps determine the CT's health. It is essential to conduct these tests under controlled environmental conditions since temperature variations can impact resistance readings. Typically, these tests should be performed as part of regular maintenance schedules or when a fault is suspected. From an authoritative perspective, the importance of winding resistance testing is underscored by industry standards and guidelines, such as those from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). These bodies provide detailed protocols to ensure that testing methods are standardized and results are reliable. In terms of trustworthiness, manufacturers often advise that new CTs undergo winding resistance tests before installation. This initial benchmark helps track any degradation over time. Additionally, documenting test results and trends can provide invaluable data for predictive maintenance strategies. In conclusion, the winding resistance test of current transformers is an essential practice that guarantees electrical systems' safety and efficiency. By regularly performing this test, one can preemptively identify potential issues and maintain the integrity of the power distribution network. A commitment to such proactive maintenance aligns with the principles of reliability-centered maintenance and underscores the dedication to operational excellence in the management and deployment of electrical infrastructure.

The test procedure includes connecting the micro-ohmmeter across the CT’s winding terminals and then recording the resistance reading. Comparing these measurements with the manufacturer's specifications helps determine the CT's health. It is essential to conduct these tests under controlled environmental conditions since temperature variations can impact resistance readings. Typically, these tests should be performed as part of regular maintenance schedules or when a fault is suspected. From an authoritative perspective, the importance of winding resistance testing is underscored by industry standards and guidelines, such as those from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). These bodies provide detailed protocols to ensure that testing methods are standardized and results are reliable. In terms of trustworthiness, manufacturers often advise that new CTs undergo winding resistance tests before installation. This initial benchmark helps track any degradation over time. Additionally, documenting test results and trends can provide invaluable data for predictive maintenance strategies. In conclusion, the winding resistance test of current transformers is an essential practice that guarantees electrical systems' safety and efficiency. By regularly performing this test, one can preemptively identify potential issues and maintain the integrity of the power distribution network. A commitment to such proactive maintenance aligns with the principles of reliability-centered maintenance and underscores the dedication to operational excellence in the management and deployment of electrical infrastructure.
Previous:
Latest news
-
Testing Equipment Industry Sees Major Advancements in 2025: Smart & Precision Technologies Lead the WayNewsJun.06,2025
-
Applications of Direct Current Generators in Renewable Energy SystemsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Hipot Tester Calibration and Accuracy GuidelinesNewsJun.05,2025
-
Digital Circuit Breaker Analyzer Features and BenefitsNewsJun.05,2025
-
Benefits of Real-Time Power Quality Monitoring Devices for Industrial EfficiencyNewsJun.05,2025
-
Earth Fault Loop Testing in High-Rise Building Electrical SystemsNewsJun.05,2025



